MOH LICENSE FOR NURSING & MEDICAL PROFESSIONALS
MOH Exam is a standardized licensing examination conducted by the Ministry of Health and Prevention (MOHAP) in the UAE for healthcare professionals who wish to practice in the Northern Emirates. purpose of the exam in ensuring that healthcare practitioners meet the required standards of competence and knowledge to provide safe and effective care in the UAE. healthcare professionals required to take the MOH exam, including doctors, nurses, dentists, pharmacists, and allied health professionals.

MOH Exam (MOH)
The Ministry of Health exam is a test that is required for health care professionals to work in Dubai, UAE. Find out more.
MOH Dataflow (PSV)
MOH dataflow registration for doctors, MOH dataflow for dentists, technicians, nurses, and pharmacists Find out more.
MOH Licensing
The MOH license is issued by the Ministry of Health and Prevention. Find out more about what it involves here.
GET ASSISTANCE FOR MOH LICENSE
GET PROFESSIONAL MOH LICENSES IN THE UAE - MOH Medical professionals wishing to practice in Sharjah or elsewhere in the UAE must obtain a License to Practice from the Sharjah, Ajman, etc Ministry of Health ( MOH ).
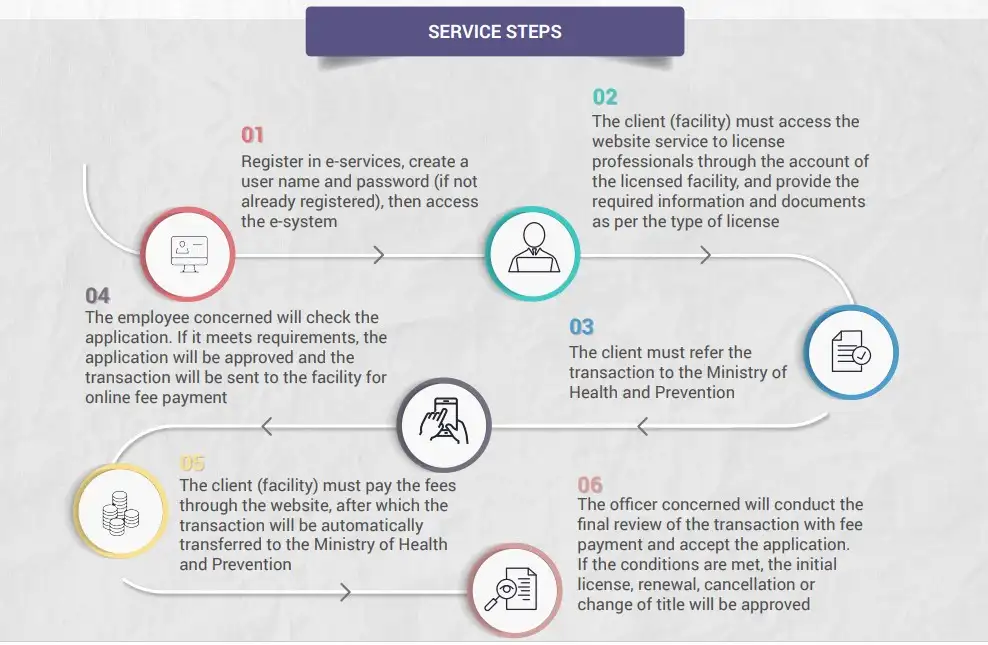
MOH LICENSING PROCESS IN UAE
- MOH Registration & licensing process
- MOH DATAFLOW Process
- LICENSE TRANSFER (MOH/DHA/HAAD)
- MOH LICENSE RENEWAL
- GOOD STANDING CERTIFICATE
- APPLY FOR A PROFESSIONAL LICENSE.
FAQ'S
Ministry of health license is for a foreigner or a resident who works in UAE. Ministry of Health License is very important in Sharjah. It is not as easy as it sounds. You need to have some qualifications to be eligible for Ministry of Health license.
Anyone who is of two years and above and has a medical degreeStructure and Format of the MOH Exam
The MOH exam, designed by the Ministry of Health and Prevention (MOHAP) in the UAE, is a comprehensive assessment to ensure that healthcare professionals meet the necessary standards to practice safely and effectively in the Northern Emirates. The exam comprises several components, each tailored to evaluate different aspects of a candidate’s knowledge, clinical skills, and professional competencies. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the structure and format of the MOH exam:
Exam Components
1. Written Exam
The written exam is typically the first step in the MOH licensing process. It is designed to test the theoretical knowledge of candidates through multiple-choice questions (MCQs).
- Format: The written exam consists of a series of MCQs, which are designed to assess the candidate’s understanding of basic medical sciences, clinical practice, and ethical scenarios relevant to their specific field.
- Areas Covered:
- Basic Medical Sciences: Questions may cover anatomy, physiology, pathology, pharmacology, and biochemistry.
- Clinical Practice: This section evaluates the candidate’s ability to apply theoretical knowledge to clinical scenarios, including diagnosis, treatment planning, and patient management.
- Ethical Scenarios: Candidates are tested on their understanding of medical ethics, patient confidentiality, and professional conduct.
The written exam typically lasts between 2 to 3 hours, depending on the specific healthcare profession. A passing score is required to move on to the next stages of the licensing process.
2. Oral Exam
For certain specializations, an oral exam is required to further assess the candidate’s clinical reasoning, decision-making skills, and communication abilities.
- Format: The oral exam is conducted as a viva voce, where candidates are interviewed by a panel of experts. During this examination, candidates may be asked to discuss clinical cases, interpret diagnostic results, and justify their treatment choices.
- Specializations Requiring Oral Exam: The oral component is often mandatory for advanced specialties such as surgery, internal medicine, and certain dental specialties. It is less common for general practice or nursing.
This exam tests not only the candidate’s knowledge but also their ability to think critically and communicate effectively under pressure.
3. Practical Exam
The practical exam component is designed to assess the hands-on skills of healthcare professionals, ensuring they can competently perform procedures and tasks relevant to their field.
- Format: Depending on the specialization, the practical exam may involve simulated patient interactions, performing specific clinical procedures, or demonstrating proficiency in technical skills using medical equipment.
- Specializations Requiring Practical Exam: Fields such as surgery, nursing, physiotherapy, and radiology often include a practical exam to verify that candidates have the necessary skills to practice safely.
This component is crucial for professions where manual dexterity and practical application of knowledge are essential.
Specializations
The structure and content of the MOH exam vary depending on the healthcare specialization. Below are some examples of how the exam is tailored to different fields:
General Medicine:
- Written Exam: Focuses on a broad range of medical conditions, diagnostics, and treatment protocols.
- Oral Exam: May include discussing complex cases or differential diagnoses.
- Practical Exam: Generally not required for general practitioners.
Nursing:
- Written Exam: Emphasizes patient care, nursing procedures, pharmacology, and ethical practice.
- Oral Exam: Rarely required for nursing; more emphasis on written and practical exams.
- Practical Exam: Tests skills such as patient assessment, administering medications, and emergency response.
Pharmacy:
- Written Exam: Covers pharmacology, pharmaceutical calculations, drug interactions, and healthcare regulations.
- Oral Exam: May include case studies where the candidate needs to advise on medication management.
- Practical Exam: Not commonly required, except for certain clinical pharmacy roles.
Allied Health Professionals:
- Written Exam: Varies widely depending on the profession (e.g., physiotherapy, radiology, laboratory technology).
- Oral Exam: Required for specialized roles where critical decision-making is involved.
- Practical Exam: Tests the ability to perform specific technical tasks, such as imaging procedures or lab tests.
Each specialization has tailored content that reflects the unique competencies required for safe and effective practice within that field. Candidates should prepare by focusing on the specific requirements and areas of knowledge pertinent to their profession.
MOH Exam Syllabus and Topics
- General Syllabus Outline: Provide an overview of the core subjects and topics covered in the MOH exam, tailored to different medical fields.
- For Doctors: Clinical medicine, surgery, pediatrics, gynecology, and other specialized areas.
- For Nurses: Nursing fundamentals, patient care, pharmacology, and medical ethics.
- For Pharmacists: Pharmacology, pharmaceutical calculations, drug interactions, and regulatory aspects.
- For Allied Health Professionals: Relevant technical knowledge and clinical skills specific to each profession.
- Reference Materials: Suggest textbooks, guidelines, and online resources recommended for preparation.
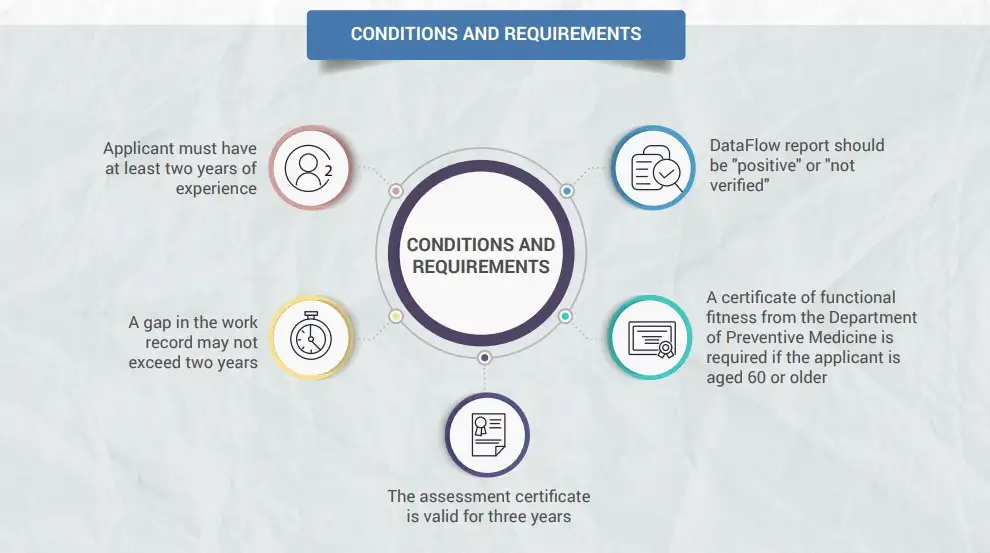
Eligibility Criteria for the MOH Exam
- Educational Requirements: Detail the minimum educational qualifications required to sit for the MOH exam, varying by profession (e.g., MBBS for doctors, B.Sc. Nursing for nurses).
- Experience Requirements: Explain the necessary clinical experience, including internships and postgraduate experience required by MOHAP.
- Documentation: List the documents required to prove eligibility, such as degree certificates, transcripts, work experience letters, and a good standing certificate.





